FlameinMind
iTHRVE CranioSacral & Coherence & Chakras APPs
Applications for iPhone 5-7 , iPod Touch 5-7 & iPad
GROUP
CranioSacral Wave & Cranio Sacral apps for iPhones
CranioSacral Wave
"CranioSacral" or "sacro cranial" wave is like a tide that craniosacral practitioners can feel all through the body. It is quite a slow rhythm wave of about 4 to 8 cycles per minute. This slow wave can be felt in the whole body, but also in each bone, in each muscle,... in each organ of the body.
In 1990, Daniel Fernandez (1), a french osteopath, was the first to demonstrate a relationship between the craniosacral wave and a blood pressure wave discovered by Siegmond Mayer which is usually called "Mayer wave" (originally defined as Traube–Hering–Mayer waves).
To be able to feel this very small pressure variation with their hands, craniosacral practitioners have to do a lot of practice to get confident with this very specific feeling. Using specialised blood pressure recordings gives, in this case, a very critical help in perceiving this.
Live recording of the blood pressure wave is not easy to achieve.
- T
Another way is to use a special armband connected to a printer. But this method only allows a continuous recording of about one minute. This was the way used by D. Fernandez in his publication (1) and this was the way that helped me to be confident with my manual palpation when I was a student.
New devices are now available to measure these blood pressure variations, but these devices are quite expensive (2) (3) (4) (5).
A few years ago, thanks to the increasing power of computers and interfaces, I tried to develop a simple and cheap device that could display the Mayer pressure wave in real time. I achieved this on a PC with an earclip light sensor, and A/D interface:
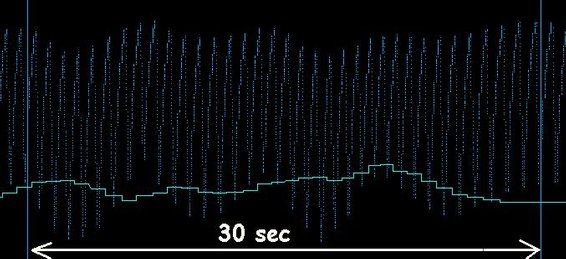
Variations of the cardiac pulsations recorded by an auricle light sensor highlighting the Mayer wave oscillations (dark blue curve). The light blue curve represents the monitoring of the variations of the cardiac rhythm (HRV). It is observed that the variation of the Mayer wave does not necessary follow the variations of the heart rate (HRV).
Recording of the cardiac Mayer wave (light blue curve). In yellow, the recording of the manual palpation. In dark blue, monitoring of respiration.
One can observe a good correlation between the upper part of the light blue curve and the manual palpation of the sacro-cranial wave (yellow curve). The lower part of the cardiac signal (light blue) follows respiration (dark blue).
Thanks to the increased power of iPhones and availability of new bluetooth sensors,
it is now possible to create a new iPhone app allowing the CranioSacral wave display in real time*
* CranioSacral wave is a blood pressure wave and can only be displayed wiith light sensor like Camera or Finger Sensor
(can not be displayed with HRV sensors like Polar Chest Strap)
Real time waves of
HRV, HRV_VLF, HRV_LF, PPG_LF
The craniosacral wave is related to
the yellow pressure curve.
Here is more information about my work on HRV, Mayer wave and sacrocranial therapy:
(1) D. FERNANDEZ, A. LECINE
L'enregistrement de l'onde de Traube-Hering et de la palpation crânienne simultanée.
Revue Ostéo n°9 - novembre 1990.
http://www.osteopathie-france.net/comprendre-losteopathie/osteo-cranien/616-cranien091
(2) KENNETH E. NELSON, DO; NICETTE SERGUEEF; CELIA M. LIPINSKI, MSII;ARINA R. CHAPMAN, MSII; THOMAS GLONEK, PhD
Cranial rhythmic impulse related to the Traube-Hering-Mayer oscillation: comparing laser-Doppler flowmetry and palpation
JAOA * Vol 101 * No 3 * March 2001 * 163
http://www.iahe.com/images/pdf/Traube.pdf
(3) Kenneth E. Nelson, DO, FAAO, FACOFP
The Primary Respiratory Mechanism
The AAO Journal Winter 2002, p24
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266617625_The_primary_respiratory_mechanism
(4) Kenneth E. Nelson, DO; Nicette Sergueef, DO (France); Thomas Glonek, PhD
Recording the Rate of the Cranial Rhythmic Impulse
JAOA * Vol 106 * No 6 * June 2006 * 337-341
http://jaoa.org/article.aspx?articleid=2093282
(5) Continuous noninvasive arterial pressure
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continuous_noninvasive_arterial_pressure
a